For over a century, Einstein's general theory of relativity has been key to understanding gravity.
But new research suggests this theory "glitches" in the farthest reaches of space.
That doesn't mean we're throwing Einstein's theory out the window. But it may need a slight tweak.
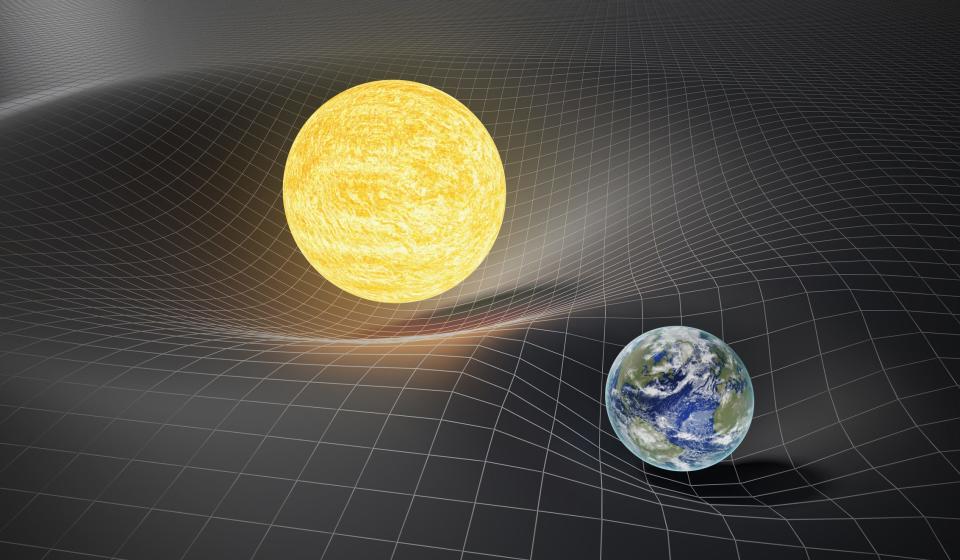
Over the last 100 years, countless studies have proven that Albert Einstein's greatest theory — his theory of general relativity — is practically bulletproof, capable of everything from predicting black holes to guiding your GPS technology.
However, as scientists arm themselves with more powerful and sophisticated technology, capable of peering into the cosmos in unprecedented detail, they see phenomena they can't explain with Einstein's theory.
Einstein's general theory of relativity states that the curvature of space-time causes gravity. But zoom out to enormous scales like clusters of galaxies spanning billions of light years across, and the laws of Einstein's gravity theory appear to change.
"It's almost as if gravity itself stops perfectly matching Einstein's theory," Robin Wen, a recent University of Waterloo graduate, said in a university press release.
Wen is part of a collaboration between the University of Waterloo and the University of British Columbia who are on the hunt to solve the mystery, calling this discrepancy in Einstein's theory a "cosmic glitch."
Their new study, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, suggests that gravity becomes about 1% weaker at very large scales. If gravity behaved according to Einstein's theory, then this 1% difference shouldn't exist.
Cosmologists won't be doing away with general relativity anytime soon. It's still a strikingly accurate framework for understanding gravity at smaller scales.
"It's not like we're breaking how your GPS works, or a black hole. We were only trying to see if there's any deviation at the largest possible scales," Wen told Business Insider.
If this glitch truly exists, it could help cosmologists explain some of the greatest mysteries of the universe.
Easing cosmological tension
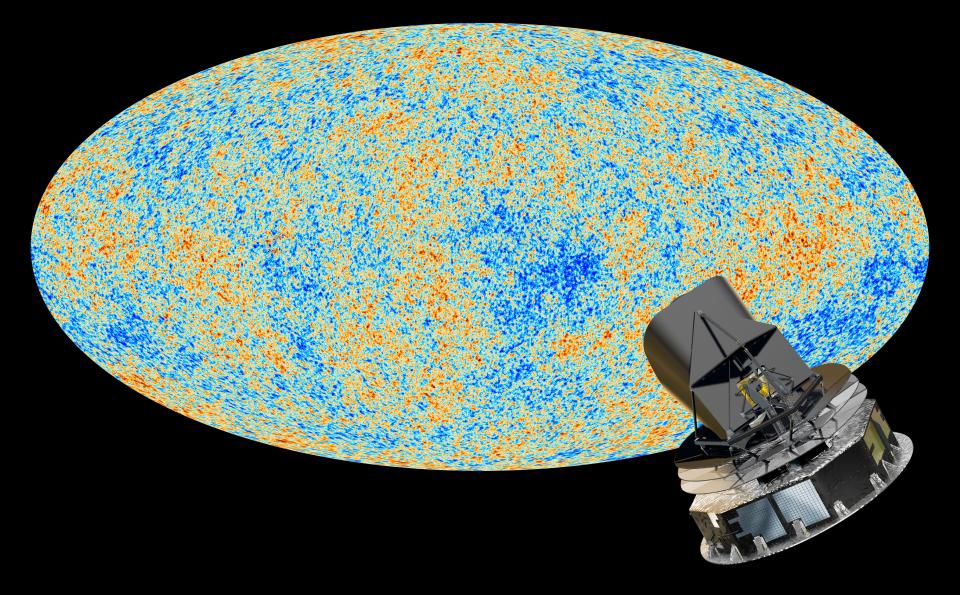
The research team was combing through data of the cosmic microwave background when they discovered this apparent glitch.
The cosmic microwave background is a vast expanse of lingering radiation that was left behind by the Big Bang. Scientists use it to understand the earliest stages of the universe like how the first galaxies formed and what happened immediately after the Big Bang.
Wen and his colleagues used a model — based on fundamental physical laws like Einstein's theory of general relativity — and compared their model's prediction of what the CMB data should look like with observational CMB data.
Their scientific model didn't match the observations — what we actually see in the distant universe.
However, when they tweaked Einstein's theory to account for a 1% gravity deficit, their model aligned more closely with the observational data, Wen told BI over email.
A 1% adjustment may not sound like a big deal, but it's enough to suggest that Einstein's theory may need a rethink. And what's more, this glitch may help us better understand some confusing behavior in the universe.
The cosmos, as we understand it, is filled with tensions. Sometimes, different measurements of the same phenomenon don't agree with each other. One example of this is the Hubble Tension — a problem that's puzzled astronomers for years.
The Hubble Tension refers to conflicting measurements of the expansion rate of the universe. According to our standard model of physics, the expansion rate of the universe should be the same everywhere. However, observations of the nearby universe suggest that the expansion rate is faster than regions of the distant universe. Astronomers have proposed multiple possible explanations but haven't settled on one, yet.
Now, with this cosmic glitch, there's a new explanation on the table.
A 1% weaker gravity at large scales could reduce the Hubble Tension by bringing the universe's expansion rate closer to measurements from local observations, said Niayesh Afshordi, study co-author and professor of astrophysics at the University of Waterloo, in a recent YouTube interview.
Thinking outside the box
The fact that this cosmic glitch could potentially help astronomers resolve the Hubble tension is a good sign that it may truly exist. But this study doesn't offer definitive proof of a 1% gravity deficit at large scales, Wen said.
For now, there's still a chance that this glitch could be the result of statistical error. "With future data in the coming 10 years, we should expect to see if this is actually a real detection, or just fluctuation due to your statistical power," Wen said.
Valerio Faraoni, professor of physics and interim dean of science at Bishop's University, told BI it's reasonable to think the glitch could exist because general relativity has not been tested in the distant universe.
So, "it's quite possible, at least in principle, that we don't understand gravity on the larger scale," said Faraoni, who wasn't a part of the study.
He thinks that in order to resolve conflicts between predictions and observations of our universe, we need to think outside the box. And this cosmic glitch study does exactly that.
"We probably need something outrageous," he said. "It does look exotic, it does look strange. But I think we have to be absolutely open to all these strange ideas."
Next, Wen and his colleagues will take a close look at new data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). DESI measures the effects of dark energy on the expansion rate of the universe, and has created the largest 3D map of the cosmos to date.
Moreover, DESI has found that, like gravity, dark energy doesn't behave the way astronomers expect at large cosmological scales. Wen wants to find out whether these two "glitches" are somehow linked, which would provide even more evidence for a need to tweak general relativity.
But even he is skeptical of general relativity's limitations. "If you asked me to bet on something, I might bet on GR still. GR works so well, right? For the alternative models, it's hard to tell at this stage," he said.
Read the original article on Business Insider